A Comprehensive Guide to Classes, Variables, Keywords , Methods, Modifiers and the Main Method in Java
A Comprehensive Guide to Classes, Variables, Keywords , Methods, Modifiers and the Main Method in Java
Class
A blueprint used to create an object is called a class. Various
objects can be created related to one class. The limit of the class is only the
class, the constructor of the class, and the main method. The methods of the class do not belong to the
limits of the class.
If you want to know more about class read this blog post.
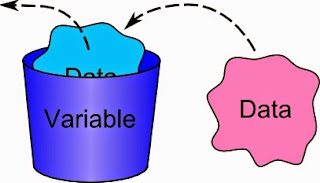
Variable
In Java, a variable is a
storage location used to store information that can be changed during program
execution. That is, a variable is a
named storage location where data is stored and can be referenced and
manipulated in a program. There are two
types of variables in Java. Variables
are governed by the type of data they can hold.
Static
A static variable in Java is a class variable declared using the
static keyword. It is associated with
the class itself, and only one copy of the static variable is shared among all
instances of the class. It can also be
called a variable that belongs to the class rather than any specific instance
of the class. This variable is accessed anywhere in the class.
Keypoints👇
👉Changes made to a static variable in one instance are represented in all instances and all instances of the class share the same static variable.
👉The class name is used to access static variables.
👉 Static variables can be
modified directly using the class name or through an instance of the class, but
sometimes doing so creates confusion, so static variables are accessed and
modified using the class name.
👉Static variables are used to represent properties that are shared across all instances of a class.
Local variable
In Java, a local variable is a variable inside a method, that is,
a variable declared inside a constructor or code block. Local variables must be explicitly declared
and initialized before they are used.
Local variables can only be accessed within the scope in which they are
defined. And they remain for the
duration of that scope and once the scope goes out, the local variable goes out
of scope and reclaims its memory.
Key points 👇
👉 Local variables are
accessible only within the code block in which they are declared. They have a limited scope. Attempting to
access them outside that scope will result in a compilation error.
👉Local variables must be explicitly initialized before they can be used. Attempting to use an uninitialized local variable will result in a compilation error.
👉The lifetime of a local
variable is limited to the block duration of the code in which it is
declared. Once the code exits the block,
the local variable is no longer accessible, and its memory is reclaimed.
👉Each invocation of a method or code block gets its own local
variables. This makes local variables
thread safe in the context of method execution.
Instance variable
An instance variable is a variable that
belongs to a specific instance of a class. Instance variables are used to store
data that is unique to each instance of the class.
It is a variable in the limit of the
class.
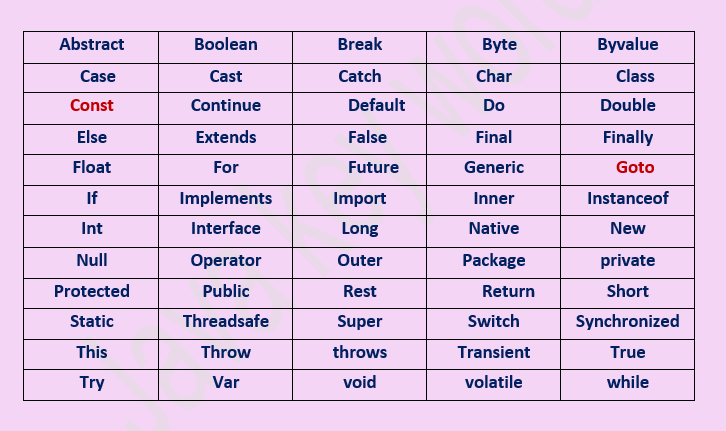
Keywords
Keywords are an integral part of the
Java programming language and are reserved words that have special meanings and
cannot be used as identifiers . They are used to define various elements and
functions. Some keywords, like Const, Goto are currently don't have any functionality in
the language.
Method
A group of codes that perform a specific task or
operation is called this. Methods are
defined within classes and are used to organize and structure code. They encapsulate functionality, making code
modular and reusable.
Modifiers
Modifiers are keywords that provide
additional information about classes, variables, and methods. They are used to
control access, visibility, and behavior of these elements. There are two main
categories of modifiers in Java,
Non Access
Modifier
Static
The element belongs to the class
rather than to instances of the class. For methods, it means the method can be
called without creating an instance of the class.
Access Modifier
Private
The element is accessible only within its own class.
default (no modifier)
The element is accessible only within its own package.
Protected
The element is accessible within its own package and by subclasses.
Public
The element is accessible from any other class.
Main Method
The main method is the entry point of
a Java program.
public
The main method
must be public so that it can be accessed by the JVM.
static
The main method
must be declared as static because it is called by the JVM before any objects are
created.
void
The main method
does not return any value.
main
This is the name of the method. The JVM looks for a method with exactly this signature when starting the program.
String[] args
The main method
takes an array of strings as its parameter. This parameter allows you to pass
command-line arguments to your Java program.
The args parameter is an array of strings
where each element contains a command-line argument.
Article by-: Rasanjali
Herath
E-Mail-: rasanjaliherath899@gmail.com









Comments
Post a Comment