A Guide to Object Generating, Data Types, Parameters and Arguments
A Guide to Object Generating, Data Types, Parameters and Arguments
In Java programming, Object Generation involves creating
objects based on classes, shaping the structure of the code. Data Types define
the nature of values – numbers, words, or complex structures – ensuring
accuracy and efficiency. Parameters act as instructions for functions, and
Arguments are the actual values that bring these instructions to life, making
code adaptable and powerful.
01.Object Generating
In Java, "object generation" refers to the
creation of objects, which are instances of classes in the Java programming
language.
Class
In Java, a class is like a blueprint or template that describes how to create objects. It defines the properties (data) and behaviors (methods) that objects of that type will have.
Object
An object is an instance of a class. It's like a
specific copy created based on the blueprint provided by the class. Objects
have their own set of data and can perform actions defined by the class.
Generation
Generating objects means making new instances of
a class. We use the class as a template to create actual objects in our
program.
In Java, the 'new' keyword is commonly used for object
generation.
 Here, 'Buddy' is an object of the 'Bird' class, and 'new
Bird() 'is the process of creating
(generating) a new instance of the 'Bird' class.
Here, 'Buddy' is an object of the 'Bird' class, and 'new
Bird() 'is the process of creating
(generating) a new instance of the 'Bird' class.02.DataTypes
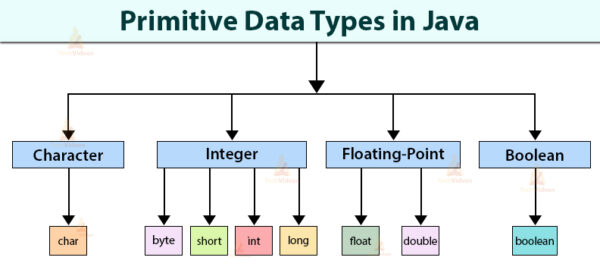
In Java, data types define the types of values that
variables can hold. They specify the size and format of the data that can be
stored in a variable. Java has two categories of data types: Primitive data
types and Reference data types.
02.1.Primitive Data
₁.Boolean
The 'boolean' data type in Java
represents a binary value, typically used to indicate true or false conditions.
Booleans are fundamental for decision-making in programs, such as in
conditional statements and loops.
Example:
boolean isRainingToDay= true;
₂.Byte
The 'byte' data type in Java is an 8-bit signed integer. It
can represent integer values from -128 to 127. 'byte' data type used to store small integer values in a memory-efficient
way.
Example:
byte numByte = 42;
₃.Char
The 'char' data type in Java is
used to represent a single character. It's a 16-bit Unicode character, allowing
it to store a wide range of characters, including letters, digits, symbols, and
special characters.
Example:
char numChar = 'A';
₄.Short
The 'short' data type is suitable
for scenarios where memory efficiency is crucial, and the required range of
values fits within its limits.The 'short' data type in Java is a 16-bit signed
integer, allowing it to store a range of values from -32,768 to 32,767. It's
often used when we need a larger range of values compared to a 'byte' but want
to conserve memory compared to an 'int'.
Example:
short numShort = 32000;
₅.Int
The 'int' data type is commonly
used for storing integer values in various computations and scenarios where
precision beyond whole numbers is not required. The 'int' data type in Java is
a 32-bit signed integer, capable of representing a wide range of whole numbers.
Example:
int numInt = 123456;
₆.Long
The 'long' data type is used when
dealing with large integer values that exceed the range of the 'int' data type.
Note the use of the 'L' suffix to denote a 'long' literal.The 'long' data type
in Java is a 64-bit signed integer, providing a wider range than the 'int' data
type.
Example:
long numLong = 987654321L;
₇.Float
The 'float' data type is used when precision is not critical, and memory efficiency is important. Note the use of the 'f' suffix to denote a `float` literal. For higher precision, consider using the 'double' data type.The 'float' data type in Java is a 32-bit floating-point type, used to represent decimal numbers with single-precision. It's suitable for values with fractional parts.
Example:
float numFloat = 3.14f;
₈.Double
The 'double' data type in Java is a 64-bit floating-point type, offering higher precision compared to the 'float' data type. It's commonly used for representing decimal numbers with double-precision.
Example:
double numDouble = 2.71828;
Summary of Data Types
02.2.Reference Data
Reference data types are used to store references to
objects. They don't hold the actual data but rather a reference (memory
address) to where the data is stored.
Array
In Java, an array is a data structure that allows to store
multiple values of the same type under a single variable name. Elements in the array are accessed using
indices (starting from 0), and we can modify or retrieve their values. The 'length' property gives the size of the array. Arrays are versatile for
handling collections of data in Java.
Example:
int[] myNumbers = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
Class
The String class in Java represents a sequence of characters. It's widely used for manipulating and representing textual data.
Interface
An interface in Java is a collection of abstract methods (methods without a body) and constants. It defines a contract that implementing classes must adhere to.
String
The 'String' class in Java represents a sequence of
characters. It's widely used for manipulating and representing textual data.
Example:
String name = "Aliza";
Enumeration
Enums in Java are used to represent a fixed set of constants.They provide a way to create named constant values.
03.Parameter and Arguments
In Java, " parameters and arguments" are essential concepts related to methods (functions).
Parameters
Parameters are variables that are used in a function or
method definition to represent the data that the function will work with. They
act as placeholders for values that will be provided when the function is
called.
Role:
Parameters define
the input that a method expects. They are like variables that the method uses
to perform its operations.
Example:
int addNumbers(int x, int y) {
return x + y;
}
'addNumbers' is a function that takes two parameters ('x' and 'y'). These parameters define the type and number of values the function
expects.
Arguments
Arguments are the actual values that are passed into a
function when it is called. When you call a function, you provide concrete
values for the parameters. These concrete values are the arguments. They fill
in the placeholders defined by the parameters.
Role:
Arguments provide
concrete values for the parameters. They are the specific data that the method
will operate on.
printMessage("Hello, World!");
In this example, the string "Hello, World!" is
an argument passed to the 'printMessage' method. It fills in the parameter 'message' when the method is called.
Relationship between Parameters and Arguments
👉 Parameters and arguments work together. When we define a
method, we specify parameters. When we call the method, we provide arguments
that match the parameters.
👉The number, types, and order of parameters in the method
declaration must match the number, types, and order of arguments in the method
call.
W3Schools Online Web Tutorials
Article by-: Rasanjali Herath
E-Mail-:rasanjaliherath899@gmail.com








Comments
Post a Comment